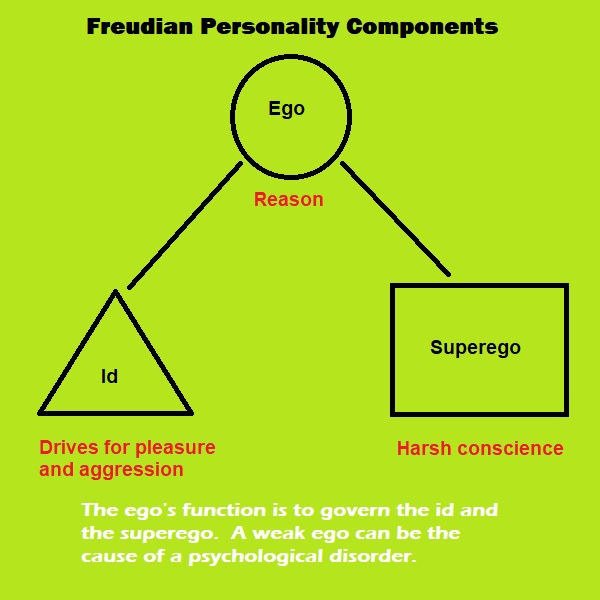
According to Dr. Sigmund Freud, there are three basic components of the human personality: the id, the superego, and the ego.
The id is that part of the personality that possesses the drives for aggression and pleasure. It consists of instincts which demand immediate satisfaction.
The superego is the personality component that determines right and wrong. It is the conscience.
Freud viewed the id and the superego as being in conflict with each other. The id impels a person to seek pleasure and gratification. The superego inflicts feelings of guilt and shame after one has done so. The id drives a person to express aggressive behavior. The superego tries to check that behavior.
The third personality component according to Freud is the ego. The ego acts as an umpire or moderator between the id and the superego. The ego is the rational part of a person's personality. Freud taught that the extent of the development of the ego during the first six years of life is critical and depends on the quality of experience during those years. Inadequate or negative child-rearing practices will result in the child developing a flawed ego that is deficient in the areas of trust, independence, or sexual identity. Limited interactions with a significant adult during the first six years of life will according to Freud inhibit the child's ego's ability to function efficiently.
Freud taught that our basic personality structures are already set by the time we are 6 or 7 years old. So, according to Freud, it is important that a parent "get it right" when rearing his or her child during the first 6 or 7 years.
The drives for pleasure or the exhibition of aggression (the id), the conscience (the superego), and the reason (the ego) are the three Freudian components of human personality. The ego governs the id and the superego. Poor interaction with a significant adult during the first six years of a child's life could lead to the development of an inefficient ego in the child's personality. A weak ego will lead to an unrestrained and conflicted id and superego.

